Imagine building powerful backend APIs without worrying about managing servers or scaling infrastructure. That is what happens when you combine Express.js with AWS Lambda. These two technologies offer a simple, cost-effective solution for modern web development. With serverless architecture, you focus on writing code, and AWS handles the rest.
In this article, we will show you how to build, deploy, and scale Express.js APIs on AWS Lambda using the Serverless Framework. By the end, you can create production-ready APIs that scale easily, saving both time and resources.
Let’s get started with serverless backend development!
Why Use Express.js on AWS Lambda?
Express.js is widely used in the Node.js ecosystem for creating RESTful APIs because of its simplicity and flexibility. AWS Lambda offers compute on demand by executing functions responding to HTTP requests, database events, and queues.
Key Advantages:
- No Infrastructure Management: Run APIs without provisioning or maintaining EC2 instances.
- Scalability: Lambda scales automatically based on the volume of requests.
- Event-driven execution: Ideal for microservices, CRON jobs, or asynchronous workflows.
- Optimized Cost: Pay only for the compute time consumed (per millisecond billing).
- Security: Seamless integration with AWS IAM, VPC, and API Gateway security policies.
This architecture lets developers focus on business logic rather than load balancers, patching, or auto-scaling groups.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, make sure you have:
- Node.js (v18.x or later)
- AWS CLI configured with appropriate credentials
- Serverless Framework installed globally
- Basic knowledge of REST API and Express.js
Step 1: Initialize a Node.js Project with Express
Create a new directory and set up the project:

Create a basic Express server in app.js:

Step 2: Adapt Express App for Lambda Execution
AWS Lambda expects a handler function. Use the serverless-http middleware to wrap the Express application.
Create handler.js:

The serverless-http library converts Express’s request/response cycle into Lambda-compatible events and contexts.
Step 3: Configure the Serverless Framework
Install the Serverless Framework globally (if not already installed):

Inside the project root, create a configuration file serverless.yml:

This configuration routes all HTTP requests to your Lambda function using a wildcard path.
Step 4: Local Development with serverless-offline
To emulate API Gateway locally, install serverless-offline:

Update your package.json with a script:

Start the local server:

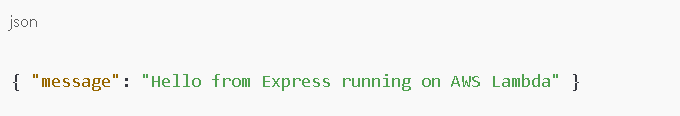
Test your endpoint:

Expected response:
Step 5: Deploy to AWS Lambda
Once validated locally, deploy to AWS:

After deployment, the CLI will return an API endpoint similar to:

This URL is now publicly accessible through API Gateway and powered by your Lambda function.
Step 6: Add Middleware for CORS and JSON Parsing
Production-grade APIs require middleware for proper parsing and cross-origin access.
Install and configure:

Update app.js:

This ensures compatibility with frontend applications and external consumers.
Considerations for Production Use
When building serverless APIs using Express, keep the following in mind:
-
Cold Start Optimization
Cold starts may introduce slight latency.
Use provisioned concurrency for consistent performance in latency-sensitive applications.
-
Deployment Packaging
AWS Lambda has a 50 MB deployment package limit (zipped).
Use webpack or esbuild to optimize and tree-shake dependencies.
-
Timeout Management
Functions timeout after 15 minutes.
For long-running processes, consider Step Functions or background processing with SQS.
-
Logging and Observability
Integrate with AWS CloudWatch Logs.
For advanced observability, use distributed tracing tools like AWS X-Ray or Datadog.
-
Secure Your API
Use API keys, JWT authentication, or AWS Cognito for access control.
Sanitize inputs to prevent injection attacks.
When Should You Use This Approach?
This architecture works well for:
- REST APIs with moderate to high request variability
- MVPs or startup applications requiring rapid iteration
- Backend services for mobile and SPA frontends
- Event-driven or microservices-based systems
- Cost-sensitive projects that don’t need persistent compute resources
Not ideal for:
- Real-time, stateful, or long-lived connections (such as chat apps using WebSockets)
- High-performance, low-latency systems where cold starts are critical
Conclusion
Running Express.js applications on AWS Lambda using the Serverless Framework is an efficient way to modernize backend APIs. It offers flexibility, reduced operational overhead, and better cost management. This setup is especially useful for organizations adopting microservices, scaling backend systems, or launching new products quickly.
At MeisterIT Systems, we help engineering teams implement scalable, secure, and efficient serverless architectures. From rapid prototyping to large-scale enterprise deployments, our solutions are designed for performance and simplicity.
Ready to launch your serverless backend?
Reach out to our experts at MeisterIT Systems to get started with a tailored solution today!