Introduction
32% of businesses use inventory management to manage their inventories.
In industries like retail, manufacturing, and warehousing, input materials and finished products are the core of business. This makes it necessary for them to maintain their inventory records that includes tracking every possible sale to avoid overstocking and minimise the risk of over spending. The one platform that can help with these functionalities and seamlessly improve your business efficiency is Inventory Management System.
If you’re anyone that runs a business related to retail, manufacturing, or any other relevant business, you must have an Inventory System to streamline your operations. And, if you’re still not sure what exactly the Inventory Management System, what it can do for your business, and how much it’s going to cost you, don’t worry!
MeisterIT Systems has got you covered! We are sharing a guide that will help you master inventory management. With this guide, you will gain insights into inventory management, understand its benefits, how to build an effective system, and discover best practices to ensure its success.
So, let’s get started!
What is an Inventory Management System?
You’ll be surprised to know that 36% of supply chain professionals use inventory management systems to achieve their business goals.
But, what exactly is the Inventory Management System?
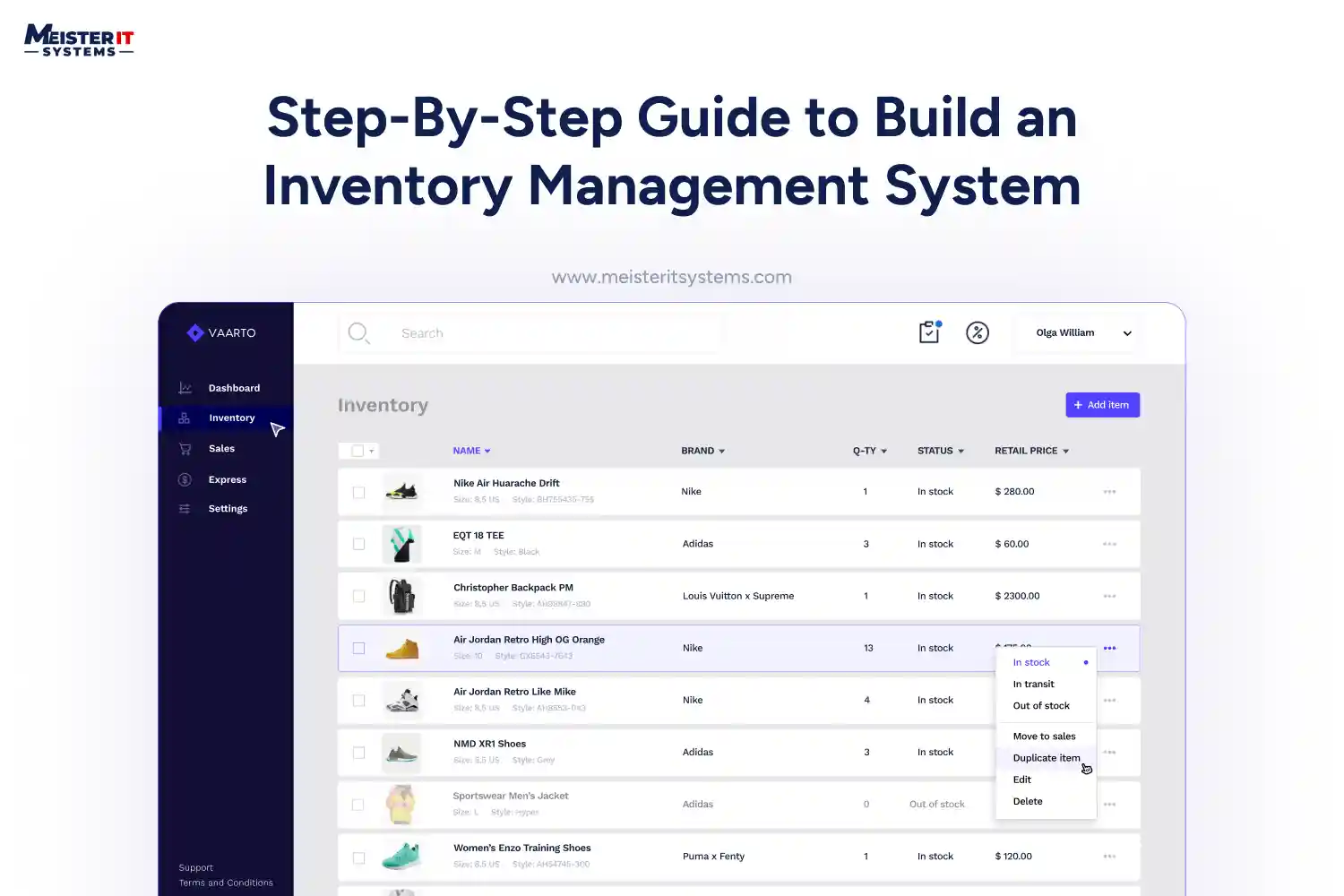
An Inventory Management System (IMS) is a software tool or technology solution designed to help businesses efficiently track, manage, and control their inventory. This includes monitoring stock levels, sales, orders, deliveries, and more. It provides a central platform for businesses to ensure they have the right amount of inventory at the right time, avoiding overstocking or running out of products.
Also, no matter whether you’re an SMB or a large enterprise, IMS has the potential to be a fundamental building block for managing your inventories.
Why is Inventory Management Important?
Approximately 34% of businesses have faced the frustrating scenario of unintentionally selling products that were out of stock.
By understanding the significance of inventory management, businesses can avoid common pitfalls like understocking and overstocking. This ensures products are consistently available to meet customers' demands and contributes to achieving long-term sales goals through accurate stock records. Moreover, efficient inventory management plays a crucial role in improving cash flow. Overstocking can tie up valuable capital that could be better utilised in other areas of the business. For instance, if you purchase 30 chairs at $10 each but can only sell 10 due to limited demand, you've invested $200 more than necessary, which can negatively impact your financial performance.
Benefits of an Inventory Management System
Approx. 17% of small businesses utilise inventory management software for managing their inventory. It helps them achieve their business goals and improve their market worth.
If you are a small business owner or part of a large organisation, and looking to build your inventory management system, then the first and foremost thing you need to do is to explore its benefits.
So, let us discuss the benefits of the Inventory Management System.
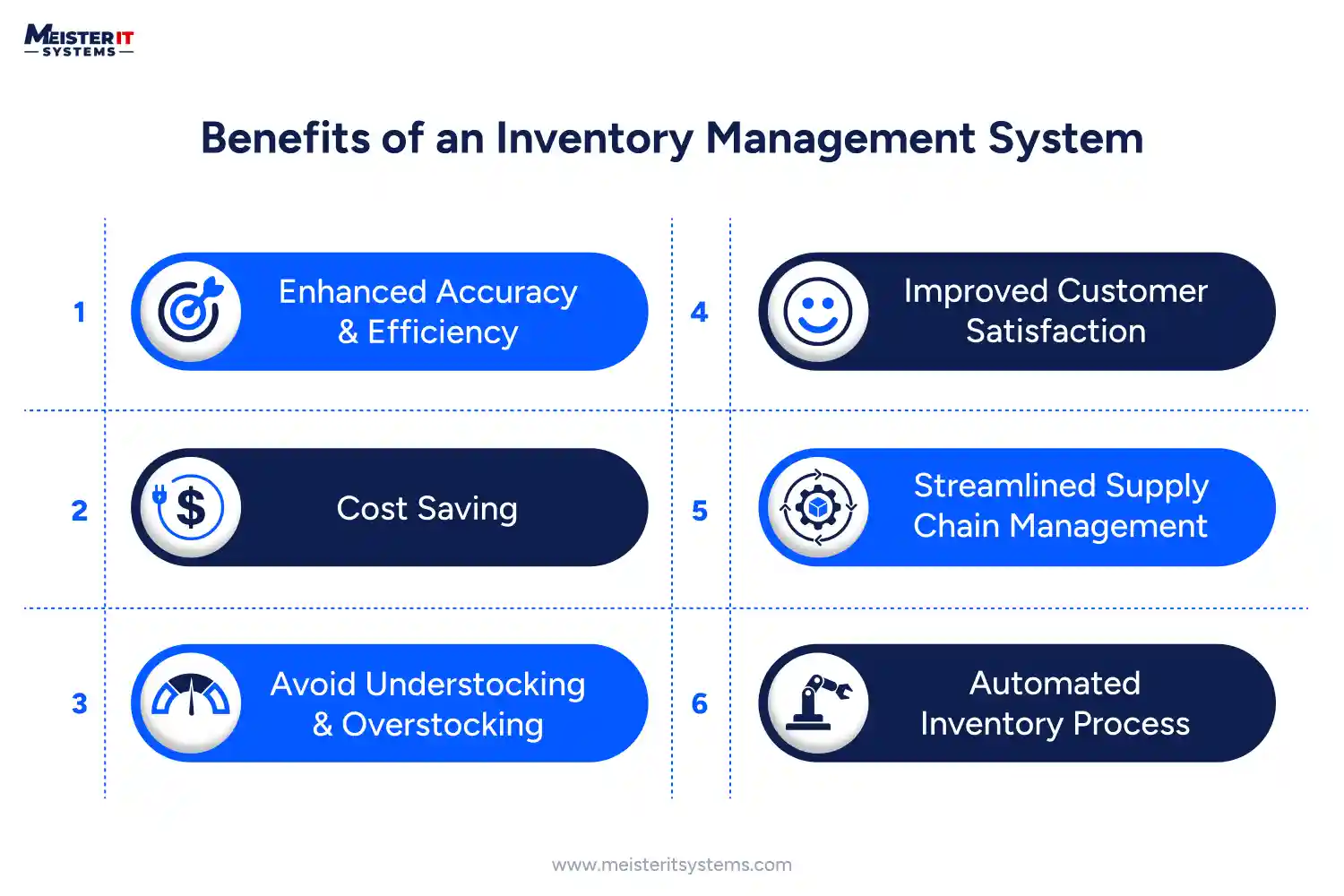
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: Inventory management helps to keep real-time records of inventory and reduce errors in stock levels. This efficiency facilitates the right decision-making while having accurate inventory.
- Cost Saving: Inventory costs include storage handling, transportation fees, insurance, and employee salaries. Because, the inventory is always at risk of theft, loss from natural disasters, or obsolescence. So, the inventory management system helps you to maintain enough stock to save costs.
- Avoiding understocking and Overstocking: Efficient planning and management prevent issues like understocking and overstocking of a product. By addressing issues like overstocking and understocking, businesses can significantly reduce inventory costs—potentially up to 10%.
- Automated Inventory Process: This modern management system automates and streamlines inventory processes like reordering, receiving, and stock counting. It lowers human error and allows employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Efficient inventory management boosts customer satisfaction by ensuring that products are available when they are required. This is attainable with real-time inventory records. With proper inventory management, you can avoid such stockouts and keep customers satisfied by meeting their needs on time.
- Streamlined Supply Chain Management: A significant 59% of companies believe that efficient supply chain management gives them a competitive edge. Because it streamlines your whole processes to satisfy customer demands, it improves operational accuracy and efficiency, contributing to the fulfilment of desired objectives.
- More Organised Warehouse: Around 42% of warehouses and distribution centres are expected to invest in technology and automation inventory management systems. It helps your warehouse to be more organised. This investment can boost production overall and decrease errors while increasing productivity.
By now, you must be aware of the inventory management system and how it’s beneficial for your business. So, now let’s talk about what it takes to develop the inventory management system.
Steps to develop Inventory Management System
Did you know?
By the end of 2024, the inventory management software market is predicted to be worth $2,191.2 million.
Giving you the right opportunity to invest in an Inventory Management Software market.
Developing a customised inventory management system needs a systematic approach , including from planning to development and implementing. Let’s talk about it detail.
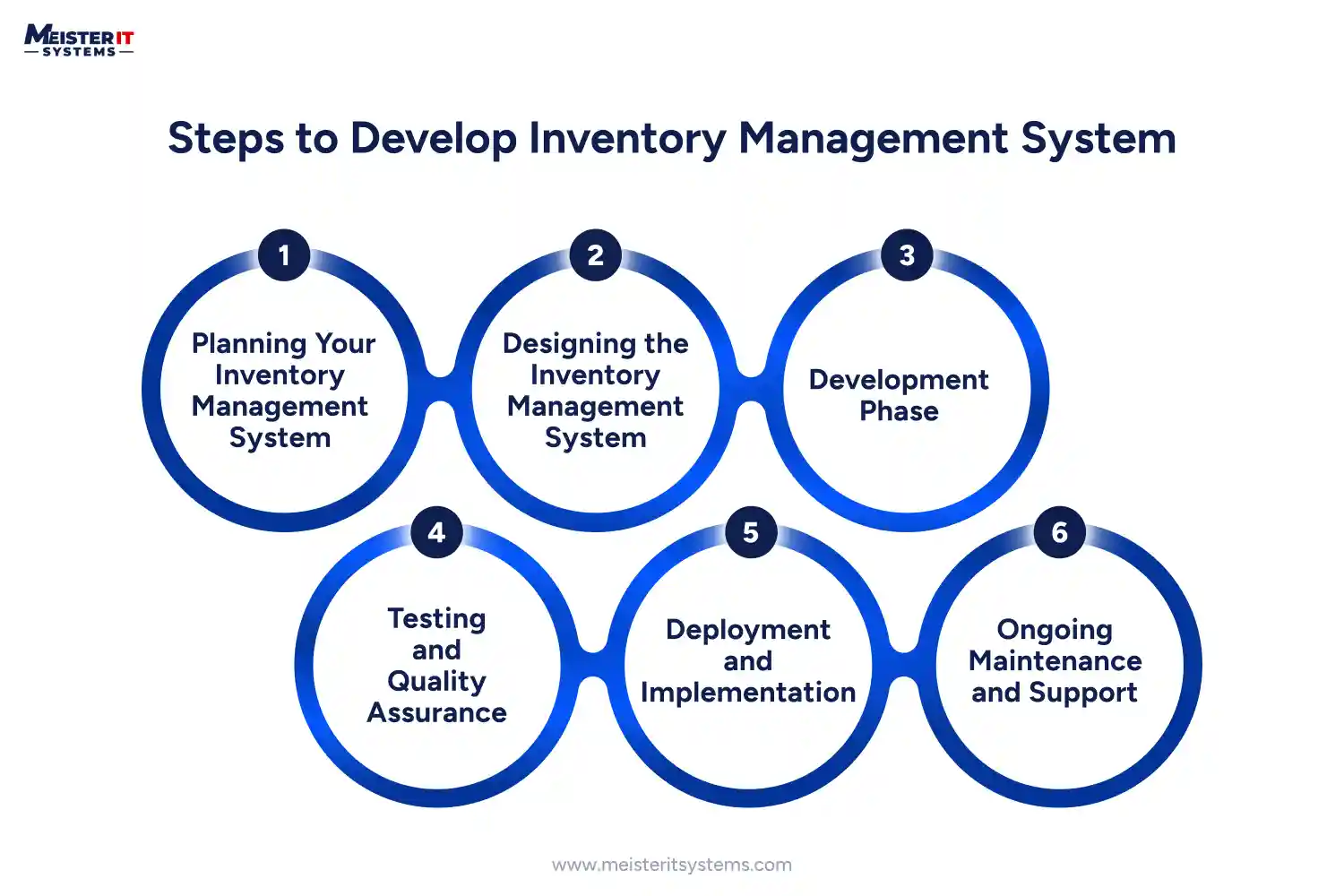
Step 1: Planning Your Inventory Management System
To adopt an inventory management system, you should prioritise effective planning. It guarantees that the solution meets your organisation's demands and can adapt to future expansion. Below is an overview of the stages involved:
Defining Your Objectives
Before setting up an inventory management system, it is critical to determine your organisation's primary and secondary goals. The initial phase should include extensive planning, with an emphasis on how the system can speed up operational workflows, improve inventory tracking accuracy, and facilitate data-driven decision-making processes. Furthermore, the system should be designed to reduce inventory-related expenses, such as those associated with overstocking or stockouts.
Furthermore, by identifying specific objectives, you can adapt the development process to efficiently achieve these goals and guarantee the system's successful implementation.
Identifying Key Features and Requirements
Once your objectives are clearly defined, outline the essential features, and needs of the inventory management system. Key features should include real-time tracking, which allows firms to accurately track stock levels, orders, and deliveries, potentially lowering inventory expenses. Furthermore, inventory forecasting can increase forecasting accuracy, reducing overstocking and stockouts and ensuring that firms maintain the optimal amount of stock at all times.
Additionally, barcode or QR code scanning ensures effective stock intake and management, decreasing manual errors by up to 43.5%. Integration with other systems, such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, or warehouse management systems (WMS), can increase operational efficiency by up to 50 percent. The system should also have thorough reporting and analytics capabilities that provide detailed insights.
Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Choosing the right technology stack is critical to building an effective and scalable inventory management system. However, your technology decision will be influenced by an array of factors, including business scale, integration requirements, database, cloud-based or on-premises system, and budget restrictions. Consider these aspects to make certain that the technology stack you select is appropriate for your inventory management system's specific objectives and goals. It is also critical to engage with IT specialists or developers to determine the best technological stack for your business's needs.
Step 2: Designing the Inventory Management System
Once you are done with planning, it's time to design your customised inventory management system to boost your business growth. Here is the breakdown to design your inventory management system
Creating a User-Friendly Interface
Approximately 73% of warehouses intend to deploy mobile inventory management technologies. Incorporating a user-friendly design will ensure that staff embrace and operate it smoothly.
A well-designed interface prioritises usability, allowing users to quickly navigate through many features without significant training. This includes features like real-time data visualisation, dashboards, and adjustable views, all of which increase user experience and productivity. The interface design should be simple and efficient, allowing both technical and non-technical users to properly manage inventory operations.
Database Design and Structure
A well-structured database is necessary for storing and retrieving massive amounts of data rapidly and precisely. It should be built to manage essential entities such as items, suppliers, orders, and customers, with appropriate linkages and indexing to allow efficient data access. The database must also allow for real-time updates to ensure that stock levels, orders, and transactions entries give the latest data. Indexing and query optimisation techniques should also be used to increase data retrieval performance.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, your customised inventory management system must be able to handle an expanding number of items, users, and locations without affecting performance. It is only possible if you consider scalability and flexibility when constructing your system. This involves the adoption of scalable technologies that enable the addition of new features while preserving existing functionality. On the other hand, flexibility is essential, as the system must be able to integrate with other platforms and respond to changes in business operations. As a result, by building for scalability and flexibility, organisations have experienced 25% faster scaling than traditional systems.
Step 3: Development Phase
Once your planning and designing phase is done, it’s time to move to the next phase i.e., development phase. This phase can be really challenging, and takes most of the time to build a system.
Setting Up the Development Environment
The initial step in the development phase is to establish an ordered development environment. This includes choosing the appropriate tools, frameworks, and version control systems to support the project. Depending on the technological stack used, developers must set up a development environment that includes code editors, dependency managers, testing frameworks, and CI/CD pipelines.
Backend Development: Building the Core Functions
The backend development phase focuses on creating the basic functionality that drives the inventory management system. This includes designing and implementing the database, creating APIs, and coding the business logic that controls inventory processes such as stock levels, order processing, and supplier management. During the backend development phase, developers should emphasise security features like authentication, role-based access control, and encryption to protect vital information.
Frontend Development: Creating an Intuitive User Interface
The frontend development phase is focused on creating an intuitive user interface (UI) that improves the user experience. This includes creating user-friendly layouts, interactive dashboards, and responsive pages that work on a variety of platforms, including PCs, tablets, and smartphones. The user interface should allow users to quickly track inventory, update stock levels, and create reports. By focusing on a clean, intuitive design, the system may reduce the learning curve and increase overall productivity for users.
Integration with Other Systems and Tools
A successful inventory management system should integrate with other business systems and tools, such as Enterprise Resource Planning solutions, accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and warehouse management systems. APIs or middleware should ensure real-time data synchronisation, improving operational efficiency and reducing manual data entry. In addition, supporting third-party tools like barcode scanners, shipping software, and CRM tools ensures the system becomes a central hub.
Step 4: Testing and Quality Assurance
The next phase of building an Inventory Management System is you should go for the testing and quality assurance to prevent structural and developmental errors. Here is the breakdown of the testing phase.
Types of Testing: Unit, Integration, and User Acceptance Testing
According to studies, early-stage testing saves 30% to 40% on issue fixes.
So, various testing methods are considered to examine the reliability of the inventory management system. Unit testing investigates individual components, whereas integration testing ensures that modules operate together. User acceptance testing (UAT) guarantees the system meets business requirements. It is also important for finding shortcomings before the system is fully installed.
Automating Testing Processes
Automating testing processes can help to streamline the testing phase and increase efficiency. Repetitive tests can be performed rapidly and accurately utilising automated technologies, resulting in speedier issue detection and resolution. However, it decreases testing time by up to 85% while assuring that all important functionalities are evaluated with minimal human involvement.
Gathering User Feedback and Making Improvements
Collecting feedback from end users helps to improve system performance. User feedback identifies around 70% of software issues, resulting in improved product-market fit and overall system enhancements. Furthermore, it promotes continual improvement and guarantees that the product satisfies user expectations. Implementing user suggestions can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Step 5: Deployment and Implementation
It's time to deploy and implement inventory management in your company after it passes the necessary testing. Here is the breakdown of deployment and implementation of an inventory management system.
Preparing for Deployment
Preparing for deployment involves creating a detailed plan that covers every aspect of the rollout. This plan is critical to minimising risks and avoiding operational disruptions. By reducing risks and downtime by up to 75%, proper preparation ensures a seamless transition. Moreover, the deployment plan should also include a well-structured testing environment that mirrors the live system, allowing for final tests to identify any last-minute issues before going live.
Data Migration and Initial Setup
Data migration is a vital phase in the implementation process since accurate data transfer is required to ensure business continuity. Improper data migration can cause significant delays, with 60% of firms facing data loss or corruption all through this process. To avoid these risks, the source data should be carefully examined, verified, and properly formatted for the new system. This phase involves transferring inventory records, product details, supplier information, and transaction histories to the new system.
Training Employees and End-Users
Training employees and end users is an essential part of the implementation process. Regardless of how smart or user-friendly the system is, its success is determined by how well employees understand and employ its features. Proper training can increase system acceptance by up to 80%, significantly reducing errors after installation. Comprehensive training programs should include interactive workshops, hands-on practice, and extensive manuals or guides that cover all aspects of the system's functionality.
Step 6: Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Once the inventory management system is deployed, ongoing maintenance and support are necessary to ensure its long-term success. So, let's discuss it below.
Monitoring System Performance
Monitoring system performance can boost system uptime by up to 20% by preventing unexpected downtime, tracking server tools, and optimising database queries. Regularly evaluating system metrics like transaction speeds, data processing times, errors rates enables the IT staff to make timely changes and increase system reliability. Furthermore, monitoring ensures that the system can handle increasing data quantities and user traffic as the business grows.
Providing Technical Supports
Providing technical support is crucial to optimise an efficient inventory management system. Because having a support crew helps you to fix the issues immediately to decrease the downtime and operational impact. According to research, systems with specialised support staff had 50% fewer issues, hence boosting overall system reliability and user confidence. Support can take several forms, including help desks, ticketing systems, and live chat, allowing users to readily report and resolve problems as they happen.
Training Employees and End-Users
Training employees and end users is an essential part of the implementation process. Regardless of how smart or user-friendly the system is, its success is determined by how well employees understand and employ its features. Proper training can increase system acceptance by up to 80%, significantly reducing errors after installation. Comprehensive training programs should include interactive workshops, hands-on practice, and extensive manuals or guides that cover all aspects of the system's functionality.
Best Practices for Inventory Management
Implementing Real-Time Tracking
Real-time inventory tracking is one of the most effective ways to improve inventory management. By delivering continual information on stock levels, product movements, and order statuses, it reduces stock disparities by 20–30 percent. This real-time visibility enables firms to promptly recognise shortages or surpluses, lowering the risk of stockouts or overstocking. As a result, businesses can improve their order fulfilment operations, ensuring that customers receive purchases more swiftly and properly.
Utilising Data Analytics for Better Decision Making
Ultising data analytics in inventory management significantly boosts decision-making by offering insights into stock levels, sales trends, and supplier performance. Companies that use analytics expect a 10% reduction in holding expenses and a 25% improvement in stock management. These insights enable firms to make data-driven decisions about reordering, inventory replenishment cycles, and supplier selection. Predictive analytics, for example, can project future inventory demands based on historical sales data, allowing stock levels to be optimised and excess inventory reduced.
Maintaining Accurate Records and Reducing Errors
Maintaining right inventory records is critical for reducing errors and preventing mismanagement. Precise record-keeping can reduce manual errors by up to 60%, resulting in increased operational efficiency. To ensure inventory accuracy, effective practices include doing regular physical audits to confirm that digital records correspond to actual stock levels. Furthermore, employing automated reconciliation processes aids in recognising discrepancies between system data and physical inventory, allowing for faster corrections and more efficient inventory management.
Challenges in Developing an Inventory Management System
A well-managed inventory management system is crucial for your business growth and day-to-day cash flow. However, there are some challenges when developing an inventory management system. Let's discuss them below.
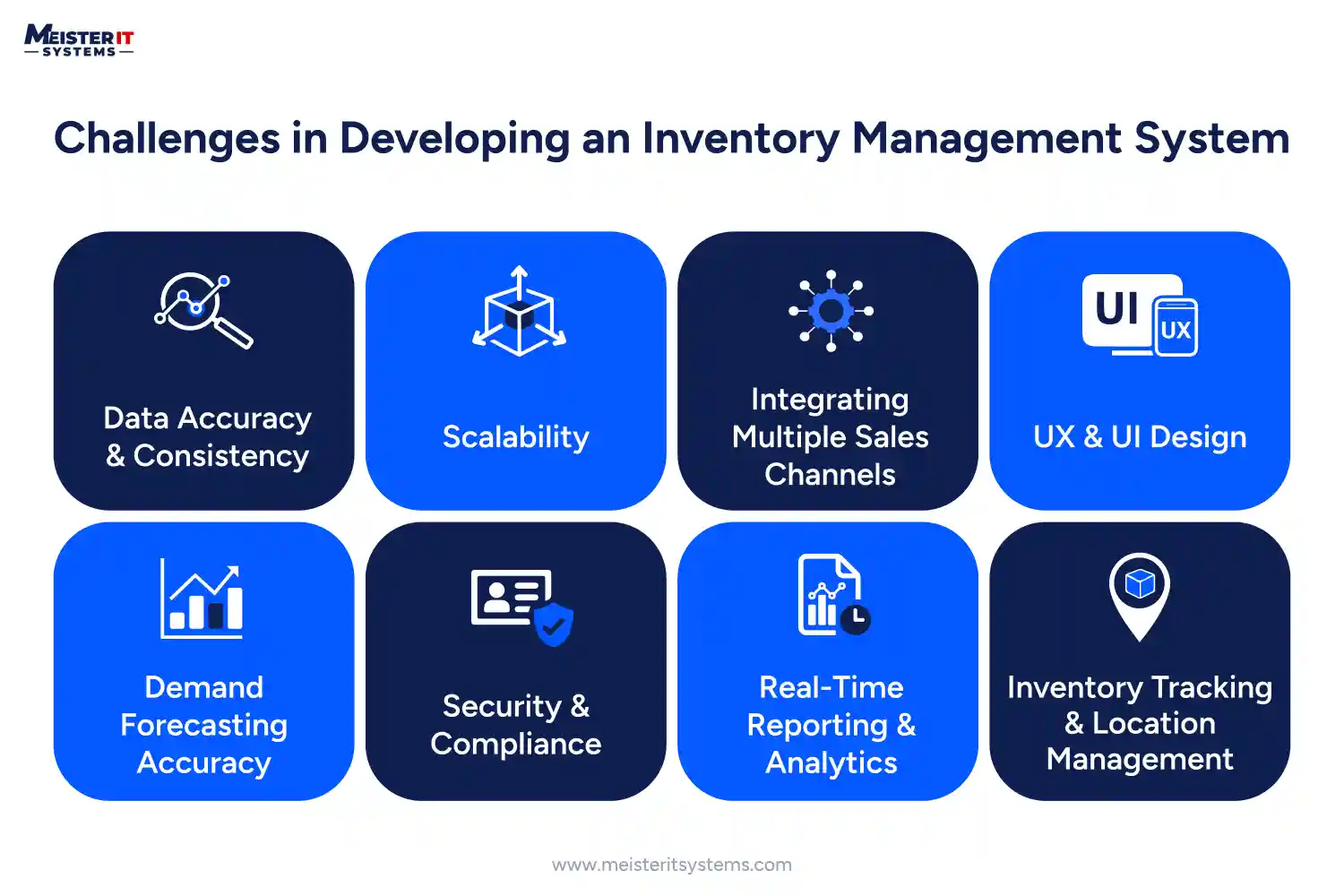
Data Accuracy & Consistency
- Problem: Ensuring accurate real-time data updates across multiple warehouses and sales channels.
- Impact: Inconsistent data might result in missing sales, overstocking, and stockouts. Discrepancies that may cause decision-making processes to be misguided arise when inventory levels are not updated precisely and promptly. As a result, there is a bad client experience and inefficient operations.
- Solution: Implement reliable real-time synchronisation solutions to ensure all data points are updated concurrently across all platforms. Use technology such as cloud computing and database replication to ensure data integrity. Regular audits and validation tests should be carried out to ensure data consistency.
Scalability
- Problem: Systems need to scale as the business grows, handling larger inventories and more complex operations.
- Impact: Poor scalability can cause slower performance and system crashes. As your company grows, the system must be able to handle an increased workload without sacrificing performance. Failure to scale effectively can disrupt business operations and result in lost revenue.
- Solution: Create a flexible, cloud-based architecture that can scale in response to increased demand. To handle increased traffic, implement load balancing and distributed computing. Make sure your system can integrate with scalable storage solutions and expand its processing power as needed.
Integrating Multiple Sales Channels
- Problem: Connecting the system to various sales platforms (online, offline, B2B) seamlessly.
- Impact: Disjointed sales channels lead to fragmented inventory data and mismanagement. Without a unified system, tracking inventory across multiple sales channels is difficult, resulting in errors and inefficiencies.
- Solution: Build APIs and integrations for smooth data flow across channels. Connect disparate systems with middleware to ensure real-time updates. Create a centralised inventory management platform that consolidates data from all sales channels to improve visibility and control.
User Experience (UX) & Interface Design
- Problem: Creating a user-friendly interface for warehouse staff and management.
- Impact: A complicated interface can lead to slow adoption and operational inefficiencies. If the system is difficult to use, employees may resist using it, resulting in errors and decreased productivity.
- Solution: Create a simple, user-friendly interface that allows for quick access to key features. Real users should test the interface to gather feedback and improve it. Ensure that the system is accessible on multiple devices, including mobile, to enhance usability in various environments.
Demand Forecasting Accuracy
- Problem: Forecasting future stock needs without proper data analytics.
- Impact: Poor forecasts lead to over/understocking and wasted resources. Inaccurate demand predictions can cause financial losses and missed sales opportunities.
- Solution: Leverage AI and machine learning for more accurate demand predictions. Use historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant data points to train forecasting models. Regularly update these models to adapt to changing market conditions and improve accuracy.
Security & Compliance
- Problem: Protecting sensitive data, especially when managing financial and customer information.
- Impact: Data breaches and non-compliance with regulations can harm your business reputation. Security vulnerabilities can lead to financial losses and legal penalties.
- Solution: Implement strong encryption, regular audits, and ensure compliance with data security standards. Use multi-factor authentication and role-based access control to enhance security. Stay updated with the latest security practices and regulatory requirements to protect your system.
Real-Time Reporting & Analytics
- Problem: Generating real-time reports for informed decision-making.
- Impact: Delayed reporting hampers fast decision-making and adaptive inventory management. Without timely insights, it becomes difficult to respond to market changes and optimise inventory levels.
- Solution: Build a real-time analytics dashboard for quick, actionable insights. Use advanced analytics tools to process and visualise data in real-time. Ensure that key metrics and KPIs are easily accessible to decision-makers.
Inventory Tracking & Location Management
- Problem: Managing and tracking inventory across multiple locations accurately.
- Impact: Misplaced items and inefficient stock movements increase operational costs. Poor inventory tracking can lead to delays, increased labour costs, and dissatisfied customers.
- Solution: Use RFID, barcoding, and GPS-based solutions for real-time location tracking. Implement automated systems for tracking inventory movements and updating records. Train staff on best practices for inventory management to minimise errors and improve efficiency.
By addressing these challenges effectively, you can develop a robust and efficient inventory management system that supports your business growth and operational excellence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an effective inventory management system is critical for today's businesses, providing major benefits such as increased operational efficiency, cost savings, and higher customer satisfaction. Prioritising detailed planning, selecting the suitable technology stack, and incorporating critical features like real-time tracking, forecasting, and seamless system integration will allow you to efficiently manage your inventory and satisfy client expectations.
And if you feel like developing an Inventory Management System for your business is overwhelming for you, it’s time to hire MeisterIT Systems (a reliable partner) who can assist you with it. We specialise in creating customised systems designed to address your specific business needs and optimise your inventory management processes.